Network segmentation can be used to isolate risky devices.Some consumer routers offer the option to create VLANs inside a larger private network. These virtual networks can be used to isolate internet-of-things devices, which researchers have repeatedly shown are full of vulnerabilities. IoT devices often expose unprotected administrative protocols to the local network so an attacker could easily break into such a device from a malware-infected computer, if both are on the same network. All networks are secured by one firewall on the perimeter of the network, and this firewall is configured to permit HTTP and SMTP traffic to pass through. Other application traffic is forced to use a secured tunnel to pass through the network.

Of course, the perimeter firewall is configured to monitor the traffic, and a log is kept for analysis. Internal network is built using Ethernet segments to reflect the infrastructure of the organization. IP network segments are then superimposed on the Ethernet segments.

Each IP network segment is secured from each other by a firewall. Each of the IP segments is connected to the layer-3 switch, thus further protecting each IP segment from an external attack. The IP traffics from the layer-3 switch are directed to pass through a Demilitarized ZONE before it enters the perimeter router. The nodes in the DMZ are DNS, SMTP, and HTTP servers, which are permitted for both inbound and outbound traffic.

The attacker would scan the ports on the perimeter firewall and look for open ports on the firewall. The firewall would have the ports such as 80 and 25 (well-known) open for Web and email services. The goal of the attacker is to find which ports in "listen," "wait," or "closed" state. Scanning tools used by both attackers and security professionals allow an automated detection of open ports. Many network-based IDS/IPS solutions, and even workstation-based endpoint security solutions can detect port scanning. It is worthwhile to investigate port scanning originating from inside the local network, as it often means a compromised device.
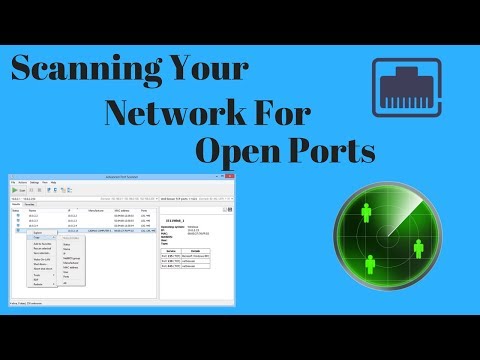
However, computers running some security solutions can generate false positives. This is beacause vendors of security solutions feature a port scanner to detect vulnerable devices inside a home network. Security across all network ports should include defense-in-depth. Close any ports you don't use, use host-based firewalls on every host, run a network-based next-generation firewall, and monitor and filter port traffic, says Norby.

Do regular port scans as part of pen tests to ensure there are no unchecked vulnerabilities on any port. Pay particular attention to SOCKS proxies or any other service you did not set up. Patch and harden any device, software, or service connected to the port until there are no dents in your networked assets' armor.

Be proactive as new vulnerabilities appear in old and new software that attackers can reach via network ports. Using an IP port open scanner can help reveal vulnerabilities attackers can potentially exploit and allow you to better understand how your network is routing. Port scans are also an important part of conducting penetration tests, such as simulating SNMP brute force attacks. Generally, firewalls and security protocols can be configured to protect ports and block traffic from attacks. Also known as filtered or dropped, this involves neither acknowledging the request nor sending a reply. No response indicates to the port scanner that a firewall likely filtered the request packet, that the port is blocked or that there is no port there.
For example, if a port is blocked or in stealth mode, a firewall will not respond to the port scanner. Interestingly, blocked ports violate TCP/IP rules of conduct, and therefore, a firewall has to suppress the computer's closed port replies. Security teams may even find that the corporate firewall has not blocked all the network ports.

For example, if port 113, used by Identification Protocol, is completely blocked, connections to some remote internet servers, such as Internet Relay Chat, may be delayed or denied altogether. For this reason, many firewall rules set port 113 to closed instead of blocking it completely. Aport scanis a method for determining which ports on a network are open. As ports on a computer are the place where information is sent and received, port scanning is analogous to knocking on doors to see if someone is home.

How Do I Protect Open Ports It is also valuable for testing network security and the strength of the system's firewall. Due to this functionality, it is also a popular reconnaissance tool for attackers seeking a weak point of access to break into a computer. The solution comes from network security applications that perform active port scanning and banner grabbing in order to determine open ports, and the applications / services behind them.

Such solutions give instant visibility into the security of your server from the outsider's perspective, by mimicking attacker's behavior. Some solutions gather extended information about the applications and services behind open ports, and also point out potential vulnerabilities which may be exploited. Port forwarding should be combined with IP filtering.Services running on a computer behind a router cannot be reached from the internet unless port forwarding rules are defined on the router.

Many software programs will attempt to open ports in the router automatically via UPnP, which is not always safe. For example, if you want to access an FTP server on your home computer from work, you can create a port forwarding rule for port 21 in your router, but only allow connections from your company's IP netblock. These cybercriminals often use port scanning as a preliminary step when targeting networks. They use the port scan to scope out the security levels of various organizations and determine who has a strong firewall and who may have a vulnerable server or network.

A number of TCP protocol techniques actually make it possible for attackers to conceal their network location and use "decoy traffic" to perform port scans without revealing any network address to the target. Some services or applications running on open ports may have poorly configured default settings or poorly configured running policies. Such applications may be the target of dictionary attacks, and, with poorly configured password policies, for example, attackers can identify credentials used by legitimate users. Furthermore, attackers can use the credentials to log into such applications, steal data, access the system, cause downtime or take control of the computer. Behind open ports, there are applications and services listening for inbound packets, waiting for connections from the outside, in order to perform their jobs. Security best practices imply the use of a firewall system that controls which ports are opened or closed on Internet-facing servers.

Additionally, security best practices advise that ports should be open only on a "need-to-be" basis, dictated by the Internet communication needs of applications and services that run on the servers. The attacker sends a SYN request to the target port over TCP. The scanner then terminates the session without establishing a connection.

If the port is closed, it responds with an RST packet, indicating that it cannot be accessed. If the port is located behind a firewall, the request does not generate a response at all. This is the most common scanning method because it does not require an established connection and is not logged by most simple event-tracking tools. On the other hand, SYN scanning requires superuser privileges on the device that sends the requests and which might not belong to the attacker. Nmap includes an advanced port scan option that is used to scan firewalls to determine their connection state and rulesets.

The TCP ACK scan (-sA) creates and sends a packet to the target with only the ACK flag set. Unfiltered systems will respond with a RST packet for both open and closed ports. If an ICMP error message or no response is received, the port is considered filtered by a firewall. Some malicious software acts as a service, waiting for connections from a remote attacker in order to give them information or control over the machine.

It is impossible to prevent the act of port scanning; anyone can select an IP address and scan it for open ports. To properly protect an enterprise network, security teams should find out what attackers would discover during a port scan of their network by running their own scan. Be aware, however, that security assessments and pen tests against many cloud hosting services, such as AWS, need approval prior to scanning. Open ports are used by applications and services and, as any piece of code, they may have vulnerabilities or bugs. The more applications and services run using open ports for Internet communication, the higher the risk of one of them having a vulnerability that can be exploited.

A bug in one service reachable from the outside may cause it to crash. Such a crash may lead to execution of arbitrary code on the affected machine, exactly what the attacker needs in order to be successful. A port scan is a series of messages sent by someone to learn which computer network services a given computer provides. Port scanners are applications that identify which ports and services are open or closed on an internet-connected device. A port scanner can send a connection request to the target computer on all 65,536 ports and record which ports respond and how. The types of responses received from the ports indicate whether they are in use or not.

As port scanning is an older technique, it requires security changes and up-to-date threat intelligence because protocols and security tools are evolving daily. Each open port may be the target of denial of service attacks. The crash of the unused NTP service causes system instability and may bring down an entire server.

Thus, an attacker can perform successful denial of service attacks on a web server, without even targeting port 80. A port is a communication endpoint where information is sent and received. Ports vary in their protocols and the types of services they offer. The most common protocols for ports are transmission control protocol and user datagram protocol . Some types of firewalls use adaptive behavior, which means they will block previously open and closed ports automatically if a suspect IP address is probing them. Firewalls also can be configured to alert administrators if they detect connection requests across a broad range of ports from a single host.

Hackers can get around this protection by conducting a port scan in strobe or stealth mode, however. Such an attack would make it difficult to trace the attacker's IP address. We have seen cases of DDOS in spite of the proxy servers' setup to protect the networks. A port scanner such as Nmap is capable of a wider variety of TCP scans that are harder to detect. Nmap allows an option for a TCP SYN stealth scan in which the third message is not an ACK but a FIN that forces the TCP connection to be closed before fully opening.

This half-open connection is not logged at the target, but may be noticed by routers or firewalls that record the original SYN packet. The next step is to sweep the target network to find live nodes by sending ping packets and waiting for response from the target nodes. ICMP messages can be blocked, so an alternative is to send a TCP or UDP packet to a port such as 80 that is frequently open, and live machines will send a SYN-ACK packet in response.

Ethernet LANs are vulnerable to attacks such as address spoofing and Layer 2 denial of service on network devices. DHCP port security features help protect the access ports on the switch against the losses of information and productivity that can result from such attacks. Businesses can also use the port scanning technique to send packets to specific ports and analyze responses for any potential vulnerability. They can then use tools like IP scanning, network mapper , and Netcat to ensure their network and systems are secure. Ports exist either in allow mode, or deny (closed; blocked) mode. If your mail server is in a state of readiness to receive SMTP traffic, we call that "listening on port 25." That means port 25 is open.

The main reason you interject a firewall between the Internet and your system is to get in the way of outsiders trying to access open ports. The applications on your network's machines can open ports without waiting for your knowledge or permission. Some, like peer-to-peer file sharing or video conferencing software, open ports with the single-minded obsession of a frenzied border collie.

Each of those open ports becomes another potential hole in your security, gullibly accepting whatever is sent to it, unless you take proactive steps to block it. Firewall configuration involves configuring domain names and Internet Protocol addresses and completing several other actions to keep firewalls secure. Firewall policy configuration is based on network types called "profiles" that can be set up with security rules to prevent cyber attacks.

Cyber threat actors use misconfigured RDP ports that are open to the Internet to gain network access. They are then in a position to potentially move laterally throughout a network, escalate privileges, access and exfiltrate sensitive information, harvest credentials, or deploy a wide variety of malware. This popular attack vector allows CTAs to maintain a low profile since they are utilizing a legitimate network service and provides them with the same functionality as any other remote user. CTAs use tools, such as the Shodan search engine, to scan the Internet for open RDP ports and then use brute force password techniques to access vulnerable networks. Compromised RDP credentials are also widely available for sale on dark web marketplaces. Nmap has two other less used port scanning command-line options that provide valuable information.

The --traceroute command-line option is performed after the scan and works with all scan types except the TCP connect scan (-sT ) and idle scan (-sI ). It uses Nmap's own traceroute algorithm and timing characteristics to determine the mostly likely port and protocol to reach the target. The --reason command-line option shows more detail about the responses from the target host, including the type of packet that was received in response to the probe. This option is also automatically enabled by the nmap debug (-d ) command-line option. The FTP bounce scan uses the FTP proxy feature on an FTP server to scan a target from the FTP server instead of your system.

The FTP proxy feature allows you to log into an FTP server and request a file to be sent to another system. By sending files to a target system and port you can determine whether a port is open or closed. Most FTP servers no longer support this functionality, but some are still available. The FTP bounce scan can be used to bypass firewalls by scanning from an organization's FTP server, which may be on an internal network, or allowed to the internal network by the firewall rules. If Nmap receives an ICMP unreachable error it will report the port as filtered.

These advanced port scanning options are stealthy and may bypass firewalls and other security controls. However, most host- and network-based intrusion detection systems will detect this type of scan activity. Keep in mind that OSes that don't follow the TCP RFC may send misleading responses. Thus, we can learn addresses for the target networks' DNS servers, Web servers, and email servers. The GFI Languard NSS software has a utility "whois" that easily allows discovering all the information regarding a domain name registered to a corporate network. DNS Zone transfers refer to learning about the servers and their IP addresses from zone files.

Is used to determine what ports a system may be listening on. This will help an attacker to determine what services may be running on the system. Some port scanners scan through ports in numeric order; some use a random order.






























